Chapter 01: Introduction¶
📖 阅读信息
阅读时间:1 分钟 | 中文字符:421
Review of Linear Algebra¶
Vectors¶
向量通常写作 \(\vec{a}\),粗体 \(\mathbf{a}\),或用起始和终止断点表示 \(\overrightarrow{AB} = B - A\)
- 能同时表示方向和长度
- 没有绝对的起始位置
Normalization¶
- 向量的大小/长度(Magnitude)记为 \(\|\mathbf{a}\|\)
- 单位向量(Unit Vector):大小为 1 的向量
- 计算任意非零向量的单位向量:\(\hat{a} = \mathbf{a} / \|\mathbf{a}\|\)
- 一般用于表示方向
Addition¶
-
几何上,平行四边形法则或三角形法则
-
代数上,就是坐标的相加
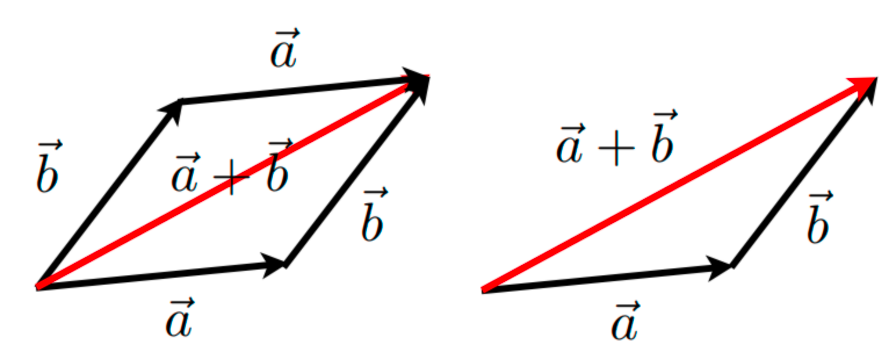
Dot Product¶
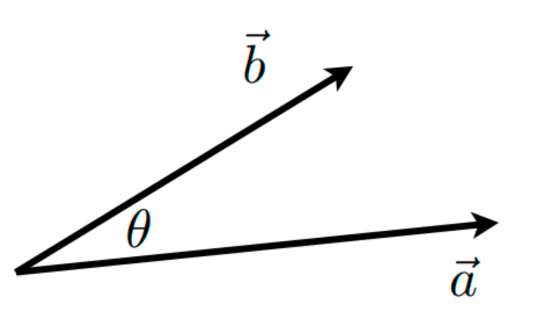
- \(\mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{b} = \|\mathbf{a}\|\|\mathbf{b}\| \cos \theta\)
- \(\cos \theta = \dfrac{\mathbf{a} \cdot \mathbf{b}}{\|\mathbf{a}\|\|\mathbf{b}\|}\)
- 对于单位向量,\(\cos \theta = \hat{a} \cdot \hat{b}\)
点积可以用于计算一个向量在另一个向量上的投影(Projection):
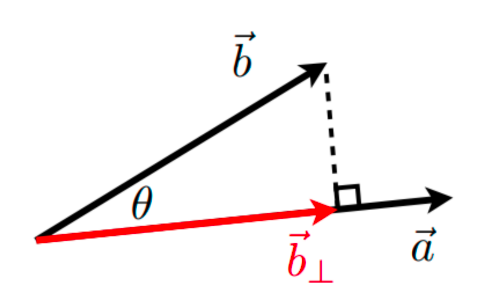
- \(\mathbf{b}_\perp\):\(\mathbf{b}\) 在 \(\mathbf{a}\) 上的投影
- \(\mathbf{b}_\perp\) 必须和 \(\mathbf{a}\)(或 \(\hat{a}\))在同一直线上,\(\mathbf{b}_\perp=k\mathbf{a}\)
- 大小 \(k = \|\mathbf{b}_\perp\| = \|\mathbf{b}\| \cos \theta\)
- \(\mathbf{b}_\perp\) 必须和 \(\mathbf{a}\)(或 \(\hat{a}\))在同一直线上,\(\mathbf{b}_\perp=k\mathbf{a}\)
Matrix¶
- 矩阵是一个 \(m \times n\)(\(m\) 行 \(n\) 列)的数组
- 带标量的加法和乘法是逐元素做的
Multiplication¶
-
矩阵-矩阵乘法:\(A \times B\) 中,\(A\)(大小为 \(M \times N\))的列数必须和 \(B\)(大小为 \(N \times P\))的行数相等(结果大小为 \(M \times P\))
\[ \begin{pmatrix}1 & 3 \\ 5 & 2 \\ 0 & 4\end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix}3 & 6 & 9 & 4 \\ 2 & 7 & 8 & 3\end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix}9 & 27 & 33 & 13 \\ 19 & 44 & 61 & 26 \\ 8 & 28 & 32 & 12\end{pmatrix} \]- 乘积中元素 \((i, j)\) 是 \(A\) 的第 \(i\) 行和 \(B\) 的第 \(j\) 列的点积
- 性质:
- 无交换律,\(AB\) 和 \(BA\) 一般是不同的
- 结合律和分配律
- \((AB)C = A(BC)\)
- \(A(B+C) = AB + AC\)
- \((A+B)C = AC + BC\)
-
矩阵-向量乘法:将向量看作是一个只有一列的矩阵(\(m \times 1\)),乘法的结果也是一个向量
\[ \begin{pmatrix}-1 & 0 \\ 0 & 1\end{pmatrix} \begin{pmatrix}x \\ y\end{pmatrix} = \begin{pmatrix}-x \\ y\end{pmatrix} \] -
每一个矩阵都可以被视为一个几何变换
Geometric Transformation
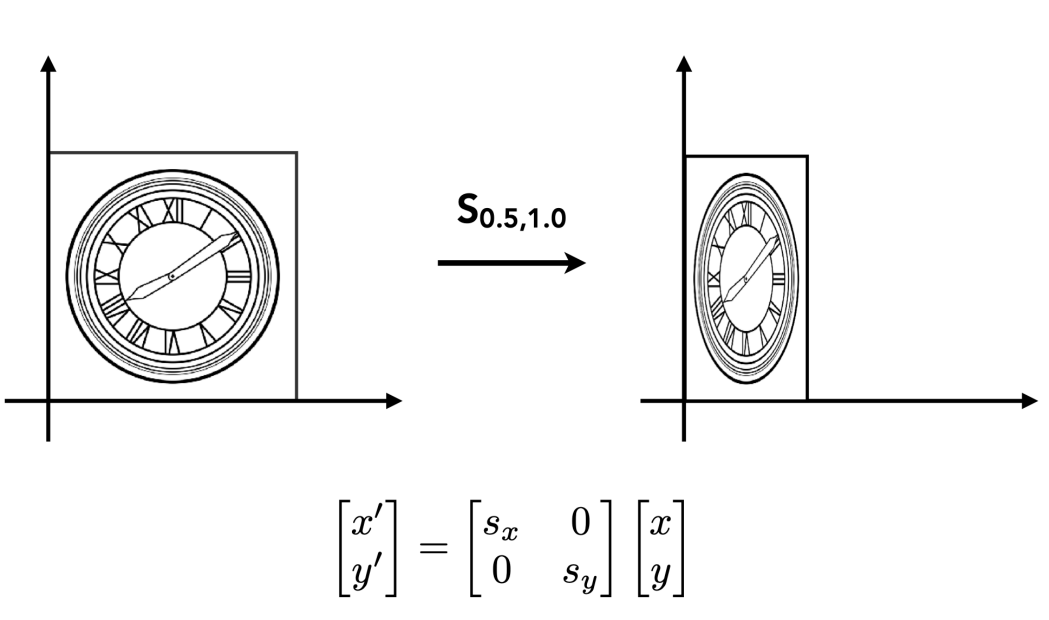
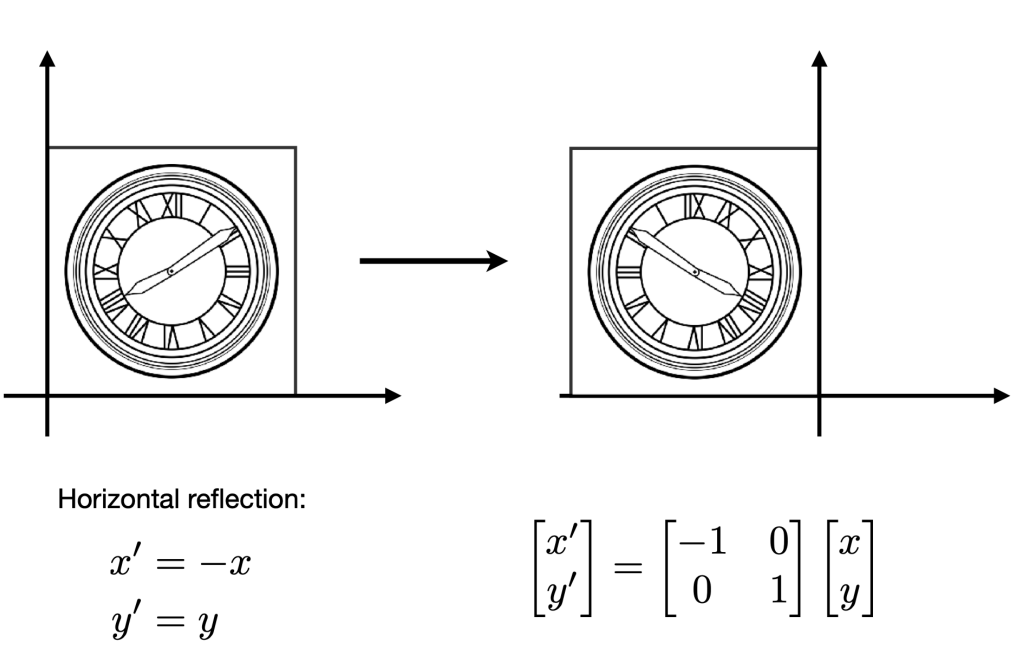
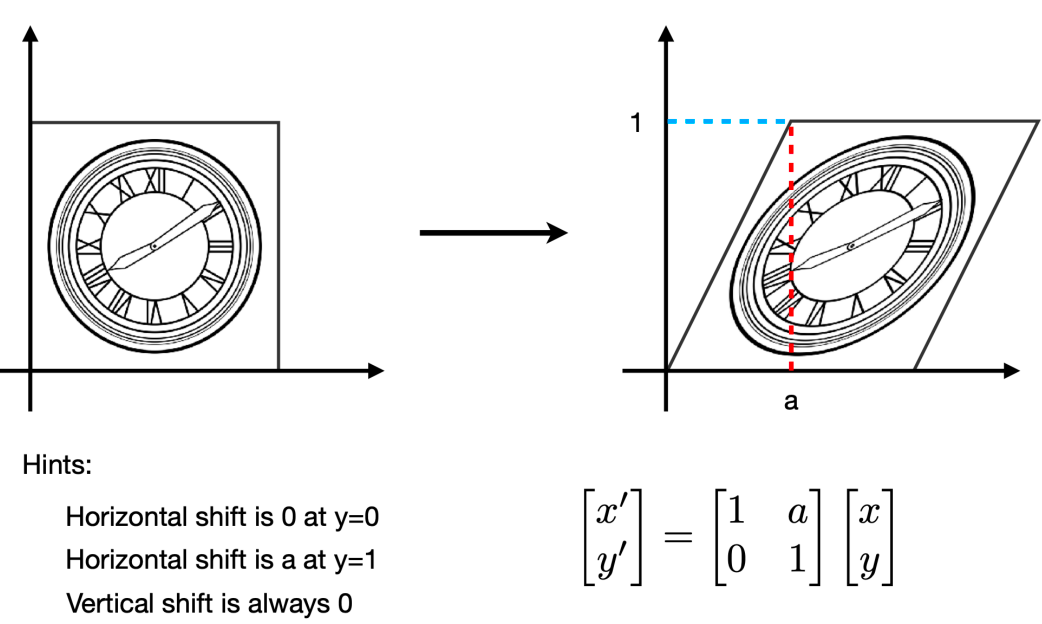
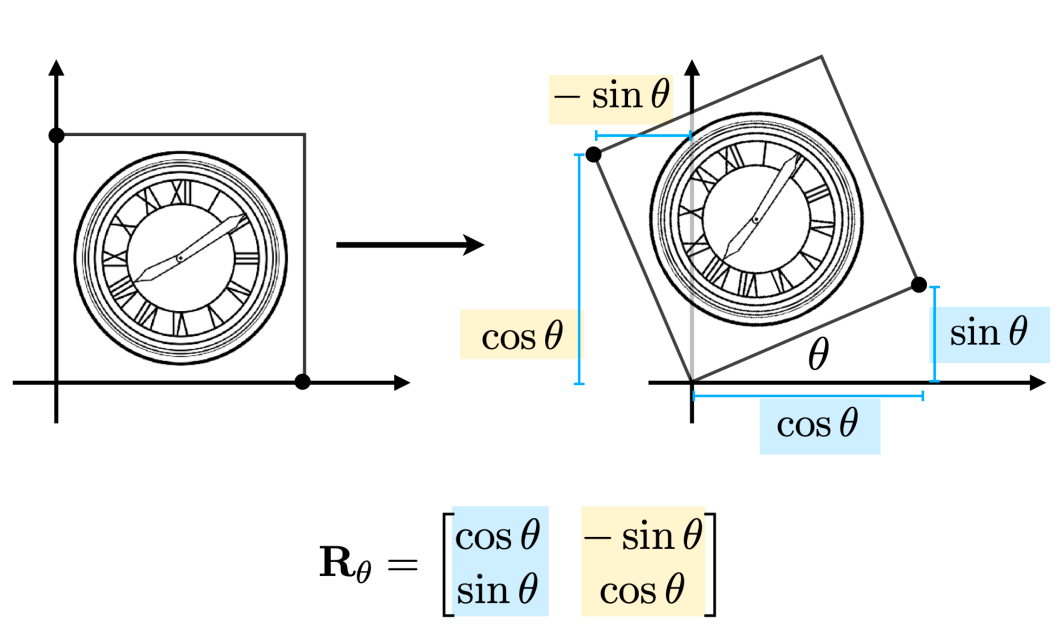
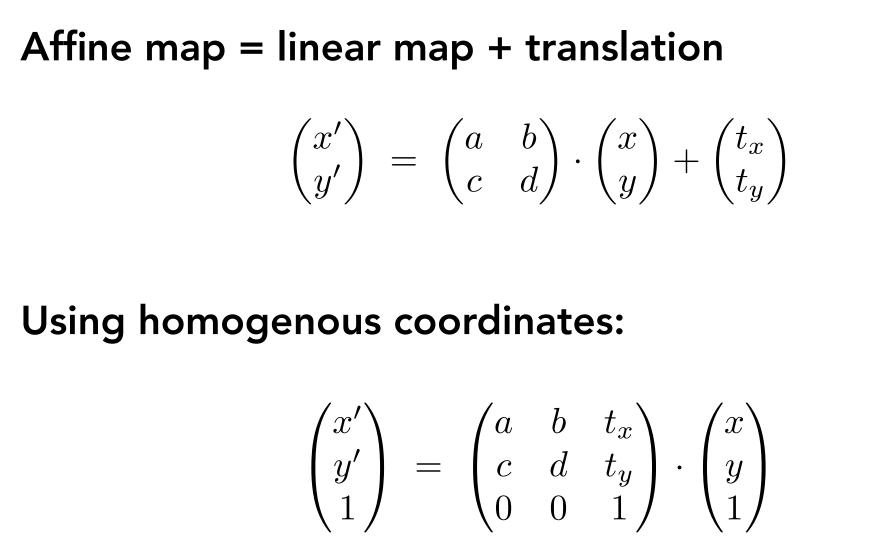
Inverse¶
- \(AA^{-1} = A^{-1}A = I\)
- \((AB)^{-1} = B^{-1} A^{-1}\)
Determinant¶
-
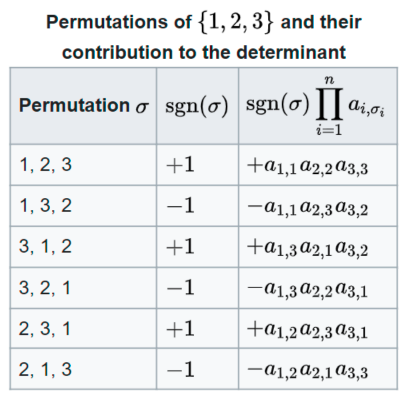
计算公式:\(\det(A) = \sum\limits_{\sigma \in S_n} \left(\text{sgn} (\sigma) \prod\limits_{i=1}^n a_{i, \sigma_i}\right)\),其中 \(S_n\) 是集合 \(\{1, 2, \dots, n\}\) 的全排列
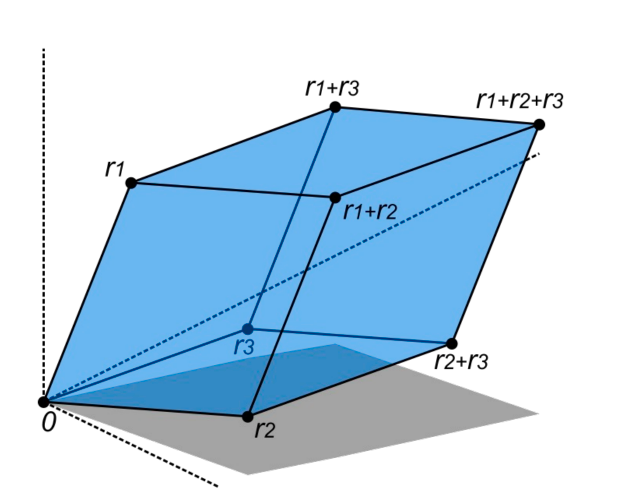
- 几何意义:行列式是 n 维平行体的体积
Eigenvalue and Eigenvector¶
-
\(Ax = \lambda x\ (A\in \mathbb{R}^{n \times n}, x \neq 0)\),其中 \(x\) 是 \(A\) 的特征向量,对应的特征值为 \(\lambda\)
-
几何意义:假如矩阵乘上某个向量后只改变这个向量的大小,方向没变(可以是相反方向),那么这个向量就是矩阵的特征向量,对应的缩放比例就是特征值
-
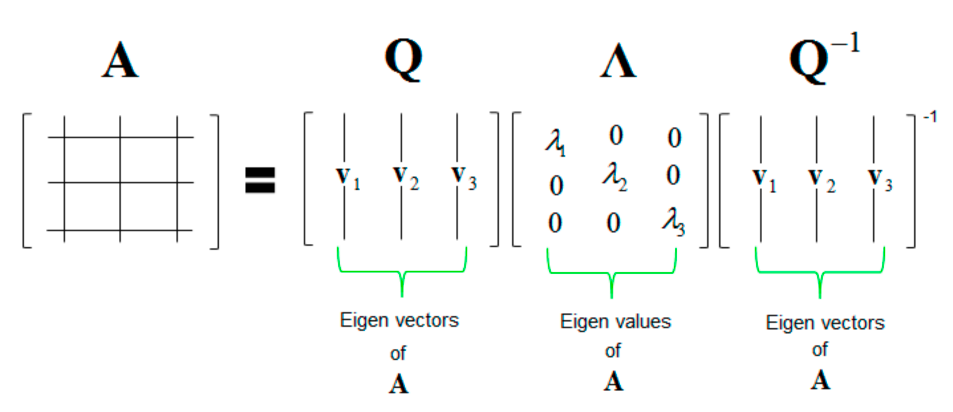
特征分解(Eigen Decomposition):
-
应用——主成分分析(Principal Component Analysis):找到数据的主方向
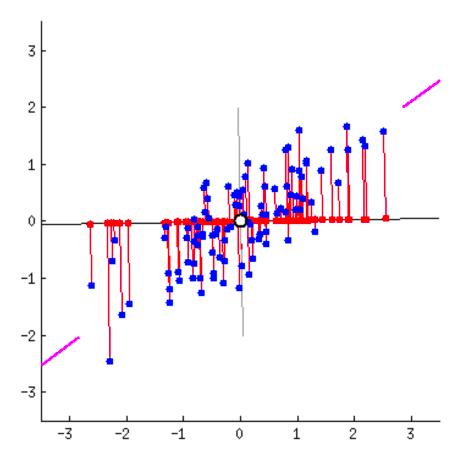
-
主成分 = \(A^T A\) 的特征向量
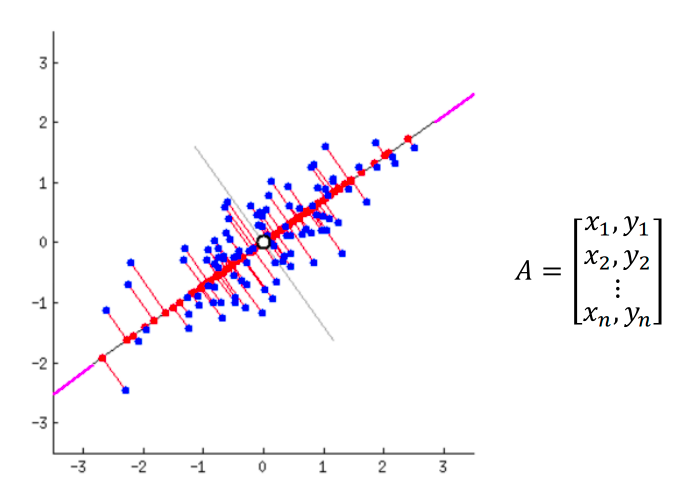
-
💬 评论
评论系统加载中...